Distillation Column Tray
Ambani Metals presents a selection of Distillation Column Trays designed for diverse separation purposes, accommodating different column dimensions. These distillation trays are easily deployable and require minimal regular maintenance. Crafted from various metallic materials using punching and bending processes, we manufacture trays tailored for applications in industries such as hydrocarbon processing, chemical, desalination, petrochemical, and gas-liquid absorption units. Our specialized Column Internals encompass Floating Valve Tray, Bubble Cap Tray, Sieve Trays, Fixed Valve Tray, and Riser & Distillation Column Hardware, catering to the varied needs of different sectors.
Distillation column tray is extensively used in the chemical process industries where large quantities of liquids have to be distilled. These are used to separate mixtures of various liquids at different temperatures. We are most trusted and reliable manufacturer and supplier of highly efficient distillation columns and trays in India.
Collaborating with our skilled process engineers, we assist you in choosing the most suitable distillation trays for your specific requirements. Furthermore, our proficient team is ready for prompt installation upon your request. Irrespective of the application, Ambani Metals offers random packing in diverse sizes and materials for distillation trays to ensure optimal performance. We provide a comprehensive array of tray sizes in common materials, all available for shipping at competitive prices.
Distillation Column Tray Types :
Global Export of Distillation Column Trays
At Ambani Metals, we specialize in the design, manufacturing, and global export of precision-engineered distillation column trays, trusted by industries around the world for their unmatched performance in separation and mass transfer applications.
Engineered for efficiency and durability, our range includes bubble cap trays, sieve trays, and valve trays, tailored for distillation columns used across refineries, petrochemical plants, pharmaceutical facilities, and chemical industries. Manufactured from high-grade stainless steel and specialty alloys, our trays are built to withstand harsh process environments while delivering superior vapor-liquid contact.
With a strong international presence, Ambani Metals proudly exports distillation column trays to key markets across:
- Middle East: Bahrain, Egypt, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates
- Africa: Morocco, Tunisia, Ghana, Nigeria, Senegal, Kenya, Mauritius, Rwanda, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia, Botswana, Eswatini, Lesotho, Namibia, and South Africa
- Europe: Germany, United Kingdom, France, Italy, Netherlands, Spain, Belgium, Poland, Czech Republic, Sweden, Denmark, Finland, Portugal, Hungary, Slovakia, Slovenia, Romania, and Austria
- Asia: Japan, South Korea, Singapore, Malaysia, Vietnam, Indonesia, Thailand, Philippines, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and Nepal
- Pan-Pacific Countries: United States, Canada, Mexico, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Peru, Panama, Australia, and New Zealand
With a focus on quality, compliance, and customer support, we ensure each export shipment meets international engineering standards and project-specific requirements. From documentation and packaging to on-time global delivery, Ambani Metals is your reliable partner for high-performance distillation column trays worldwide.
FAQs
A distillation column tray is a horizontal platform or plate within a distillation column used to facilitate the separation of liquid mixtures into individual components or fractions based on their boiling points. Trays provide surfaces where vapor and liquid phases can interact, allowing for mass transfer between the two phases. This interaction enables the separation of lighter components, which tend to rise with the vapor, from heavier components, which settle with the liquid. Trays are designed with features such as perforations, bubble caps, or Sieve designs to optimize vapor-liquid contact and enhance separation efficiency. The choice of tray design depends on factors such as feed mixture properties, desired separation efficiency, and operating conditions.
There are several types of trays commonly used in distillation columns, each designed to optimize vapor-liquid contact and enhance separation efficiency.
Sieve Trays
Sieve trays consist of perforated plates with a large number of holes. These holes allow vapor to pass through while supporting the liquid phase on the tray. Sieve trays are relatively simple in design and are widely used in distillation columns.
Sieve trays are made from a flat perforated plate which allows the passage of vapor through the liquid. They are the most economical tray option when low turndown is required. They have better anti-fouling characteristics and lower pressure drop than a valve tray or bubble cap trays. Perforations are typically 1/2" in diameter, but we can provide designs with smaller hole sizes.
Bubble Cap Trays
Bubble cap trays feature cylindrical or dome-shaped caps installed on top of the tray. Vapor rises through the caps, creating bubbles that help disperse the vapor and increase contact with the liquid. Bubble cap trays are best suited for applications with low liquid flows and/or high turndown ratios. In terms of capacity, however, they are slightly lower than a valve or sieve trays. They are also the most expensive tray option.
Fixed-Valve Trays
Fixed-valve trays feature fixed valves or slots on the tray surface. These valves or slots help control the flow of vapor and liquid across the tray, enhancing separation performance. This valve is integral with the tray deck. This is the preferred option for fouling conditions. However, it provides lower turndown and less efficiency than floating valves.
Floating Valve Trays
A floating valve tray is a type of distillation tray featuring movable valves or caps on its surface that rise and fall with changes in liquid level. These trays enhance vapor-liquid contact by allowing vapor to push the valves open, facilitating efficient mixing and separation of components in the distillation process. They are often preferred for their ability to provide better control over vapor distribution and improved separation efficiency.
Distillation column trays work by facilitating the interaction between vapor and liquid phases to separate a mixture into its individual components based on differences in boiling points. Vapor rises through the column, contacting the liquid flowing downward on the trays. This interaction allows for mass transfer between the two phases, with lighter components preferentially rising with the vapor and heavier components settling with the liquid. The trays are designed with features like perforations or bubble caps to maximize vapor-liquid contact, promoting efficient separation. The separated components are collected at different points along the column based on their volatility, resulting in the desired product fractions.
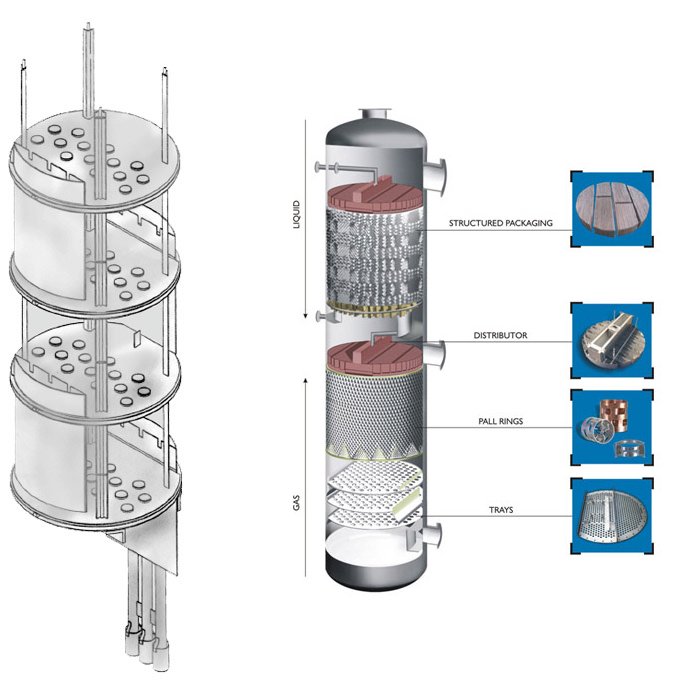
Additional Tray Design Options
For special customer requirements and/or performance of Separation Products, we offer numerous tray performance enhancing features. Some of the most common features offered by us include:
- Cartridge Trays – Suitable for small diameter body flanges. Can provide up to 5 trays per cartridge. Different sealing options are available.
- Anti-Jump Downcomer Baffles – To prevent liquids flowing across the tray from jumping over the downcomer onto the opposing flow path. Anti-Jump Downcomer Baffles are standard for multi-pass trays with center and off-center downcomers.
- Picket-Fence Weirs – These are used to decrease the effective weir height. This is for low liquid flows, and using this option will help increase the effective liquid height and prevent blowing.
- Splash Baffles – For low liquid rate services, Splash Baffles serve to maximize the liquid retention time on the trays. They can be used in place of, or in conjunction with, picket fence weirs. Splash baffles are located adjacent and parallel to the outlet weir. They clear the tray deck and outlet by 1/2" to 1" forcing the exiting liquid to flow under the baffle before it flows over the top of the outlet weir.
- Swept-Back Weirs – To reduce the effective liquid height on the tray by lowering the volume of liquid per unit length flowing over the outlet weir. This option should be considered for high liquid flow rates.
- Swept-Back Weirs - are used on side downcomers. They can also be used to balance weir loads between side and off-center downcomers in multi-pass tray designs.
- Sloped Downcomers with Recessed Inlet Sumps – Suitable for heavy liquid loads that could otherwise cause downcomer flooding.





